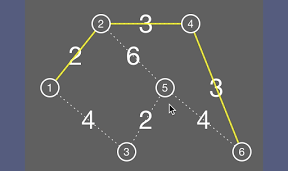
番号1からスタートした経路をベルマンフォード法で計算してみるiPhoneアプリのサンプルコードを描いてみます。
#import “ViewController.h”
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
typedef struct { int from, to, cost; } Edge;
typedef struct { int cost; vector<Edge> route; } RootPath;
#define INF 9999999
class BellmanFordSolver {
public:
vector<RootPath> solve(vector<Edge>, vector<int>);
};
vector<RootPath> BellmanFordSolver::solve(vector<Edge> edges, vector<int> v) {
vector<RootPath> rp(v.size() + 1, { .cost=INF });
rp[1].cost = 0;
while (true) {
bool update = false;
for(auto &e : edges) {
if (rp[e.from].cost != INF && rp[e.to].cost > rp[e.from].cost + e.cost) {
rp[e.to].cost = rp[e.from].cost + e.cost;
rp[e.to].route = rp[e.from].route;
rp[e.to].route.emplace_back(e);
update = true;
}
}
if (!update) break;
}
return rp;
}
@interface ViewController () {
vector<Edge> edges;
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
– (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor darkGrayColor];
CGPoint pts[] = {
CGPointMake(40, 300),
CGPointMake(120, 200),
CGPointMake(160, 400),
CGPointMake(260, 200),
CGPointMake(220, 300),
CGPointMake(340, 400)
};
edges = {
{.from=1, .to=2, .cost=2},
{.from=1, .to=3, .cost=4},
{.from=2, .to=5, .cost=6},
{.from=3, .to=5, .cost=2},
{.from=5, .to=6, .cost=4},
{.from=2, .to=4, .cost=3},
{.from=4, .to=6, .cost=3}
};
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(pts)/sizeof(CGPoint); i++) {
UIView *v = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 30, 30)];
v.tag = i + 1;
v.layer.cornerRadius = 15;
v.layer.borderColor = [UIColor whiteColor].CGColor;
v.layer.borderWidth = 2;
v.center = pts[i];
v.backgroundColor = [UIColor darkGrayColor];
v.layer.zPosition = 10;
[self.view addSubview:v];
UILabel *l = [[UILabel alloc] init];
l.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@”%d”, i+1];
l.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
l.center = CGPointMake(10, 5);
[l sizeToFit];
[v addSubview:l];
}
for (int i=0; i<edges.size(); i++) {
UIView *n0 = [self.view viewWithTag:edges[i].from];
UIView *n1 = [self.view viewWithTag:edges[i].to];
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:n0.center];
[path addLineToPoint:n1.center];
CAShapeLayer *line = [CAShapeLayer layer];
line.path = path.CGPath;
line.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor].CGColor;
line.strokeColor = [UIColor whiteColor].CGColor;
line.lineWidth = 1;
line.lineDashPattern = @[@2, @5];
[self.view.layer addSublayer:line];
UILabel *l = [[UILabel alloc] init];
l.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@”%d”, edges[i].cost];
l.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:40];
l.textColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[l sizeToFit];
l.center = CGPointMake((n0.center.x + n1.center.x) / 2.0, (n0.center.y + n1.center.y) / 2.0);
[self.view addSubview:l];
}
}
– (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {
CGPoint p = [[touches anyObject] locationInView:self.view];
UIView *selected = [self.view hitTest:p withEvent:nil];
if (selected.tag > 0) {
shared_ptr<BellmanFordSolver> cppClass(new BellmanFordSolver());
auto rp = cppClass->solve(edges, {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6});
[[self.view.layer.sublayers filteredArrayUsingPredicate:[NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@”name = %@”, @”route path”]] enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(CALayer *l, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) {
[l removeFromSuperlayer];
}];
for (auto e : rp[selected.tag].route) {
UIView *n0 = [self.view viewWithTag:e.from];
UIView *n1 = [self.view viewWithTag:e.to];
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
[path moveToPoint:n0.center];
[path addLineToPoint:n1.center];
CAShapeLayer *line = [CAShapeLayer layer];
line.path = path.CGPath;
line.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor].CGColor;
line.strokeColor = [[UIColor yellowColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.8].CGColor;
line.lineWidth = 2.5;
line.name = @”route path”;
[self.view.layer addSublayer:line];
}
}
}
@end